Blockchain: A revolutionary technology that subverts the traditional financial system and realizes
 summary:
Blockchain: A revolutionary technology that subverts the traditional financial system and...
summary:
Blockchain: A revolutionary technology that subverts the traditional financial system and... Blockchain: A revolutionary technology that subverts the traditional financial system and realizes a future of decentralization and data never tampered with!
Blockchain Technology: An Innovative and Disruptive Approach to Data Storage and Management
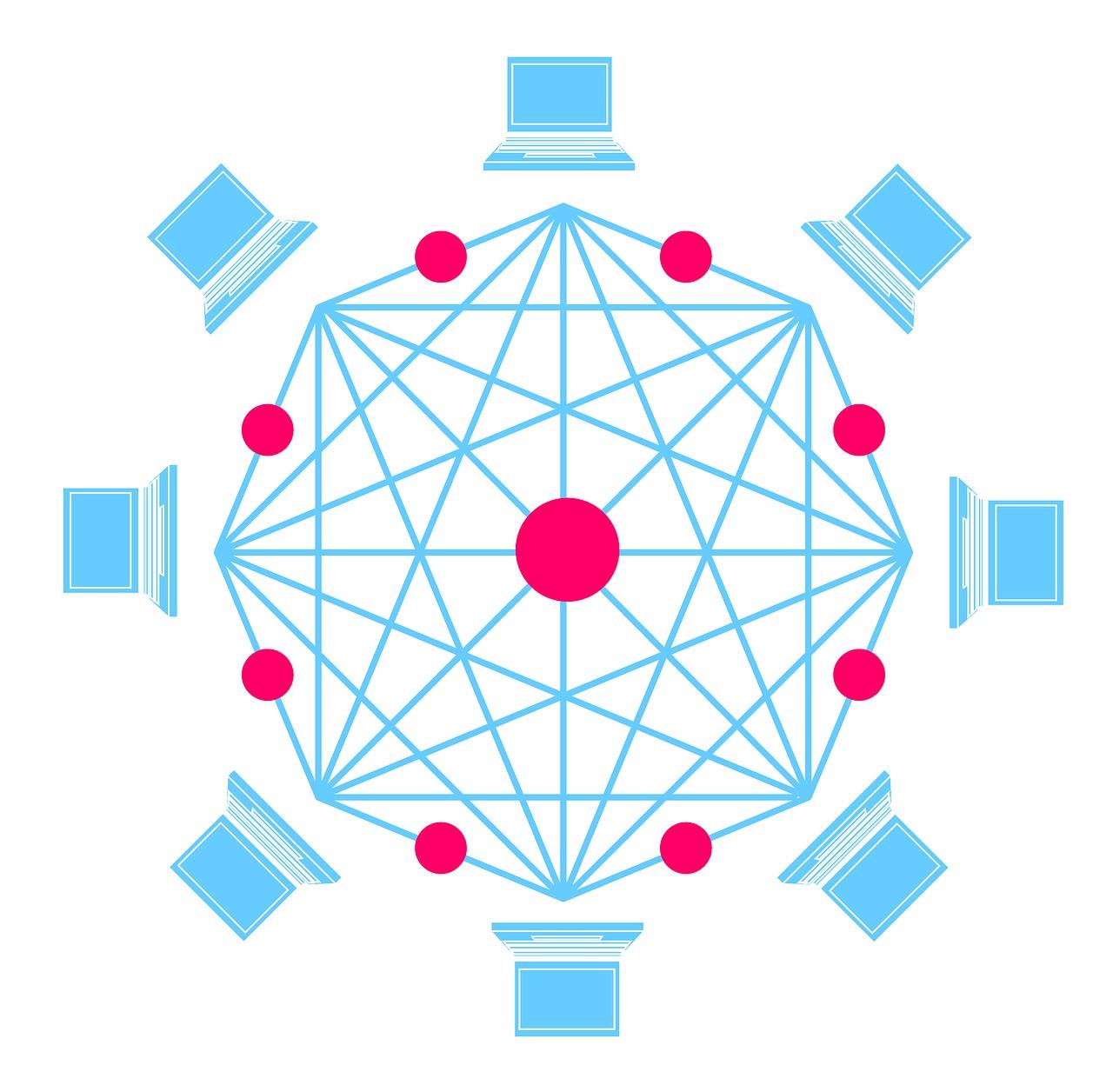
Blockchain technology is an innovative and disruptive method for storing and managing data. It was initially created to support the operation of Bitcoin. Its fundamental feature lies in its decentralized approach to storing data. Every transaction is verified and recorded in blocks, which are sequentially linked to form a continuous chain—hence the name blockchain. This technology not only underpins digital currencies but is also playing an increasingly significant role in various fields, such as finance and supply chain management.
Decentralization: The Core Feature of Blockchain
One of the core characteristics of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Traditional databases or systems typically rely on central servers or governing bodies to store and verify data. In contrast, blockchain distributes data across nodes globally, which collaborate without a central authority to maintain data integrity and security. This design eliminates the risk of a single point of failure and enhances system resilience, ensuring that the failure of any single node does not compromise the entire system.
Immutability: Ensuring Data Integrity
Another key attribute of blockchain is its immutability. Once data is written into a block and verified by multiple parties, it cannot be modified or deleted. This is achieved by embedding the cryptographic hash of the previous block in each new block. Any attempt to tamper with the blockchain is immediately detectable. This design makes blockchain ideal for recording critical, tamper-proof information, such as financial transactions, smart contracts, and identity verification records.
Proof of Work: Ensuring Consensus and Security
In blockchain operations, Proof of Work (PoW) is a primary mechanism for achieving consensus. This system requires participants to perform computations and solve complex mathematical problems to gain the right to validate new blocks. These problems demand significant computational resources, ensuring the security of the blockchain. By deterring malicious attacks, PoW guarantees the authenticity and reliability of the recorded data.
Transparency Through Openness
Blockchain is also known for its openness. The source code of most blockchain systems is publicly accessible, allowing anyone to review and audit its operations. This transparency reduces reliance on single entities or authorities, mitigating risks of errors or fraud caused by intermediaries.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
Security is another strength of blockchain technology. Data is stored in a decentralized manner across multiple nodes and is encrypted, making it significantly harder for hackers to compromise. Even if a single node is attacked, altering the data across the entire blockchain is highly challenging. Furthermore, blockchain enables anonymous transactions, requiring only encrypted addresses for transactions rather than exposing user identities. This feature is crucial for protecting user privacy.
Broad Applications Beyond Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology extends beyond cryptocurrencies and is widely applied across various industries:
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the production, transportation, and sale of goods, ensuring the authenticity and transparency of every transaction.
Finance: Blockchain offers efficient, secure cross-border payment services, reducing transaction costs and improving processing speeds.
Healthcare: Blockchain can securely store patients' health records, ensuring the safety and privacy of medical data.
The Future of Blockchain
As blockchain technology matures and its applications expand, it has the potential to revolutionize more industries and reshape how people perceive data storage and processing. By addressing trust and security challenges in existing systems, blockchain introduces unprecedented opportunities and challenges. It is poised to play an increasingly vital role in the digital world of the future.
Tags: Blockchain, Decentralization, Immutability, Security, Proof of Work